Toddler Teething: What to Expect
Phases of Teeth Growth
If your little one has passed the one-year mark and has endured the challenges of teething, you may think the discomforts of teething are behind you. Around 18 months, it often appears that they have a full complement of baby teeth. However, the two-year molars have yet to erupt.
When Do Toddlers Stop Teething
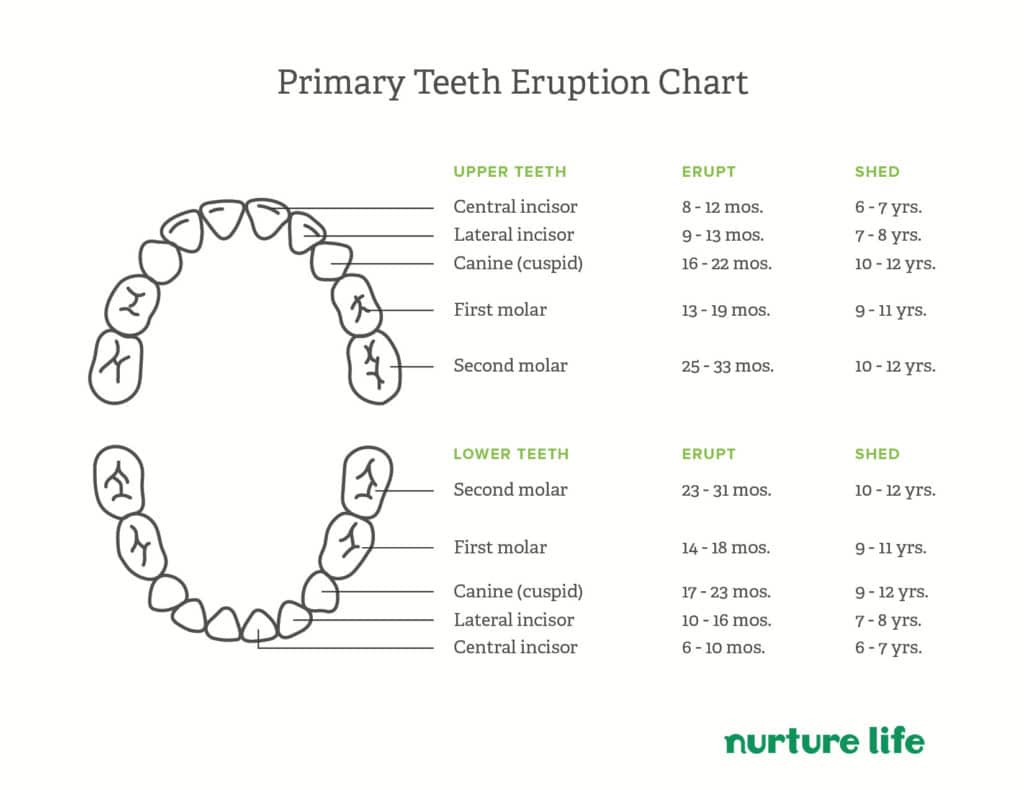
Two-year molars are your toddler’s second set of molars that emerge posterior to (that is, emerge further back in the mouth than) the molars that came in around their first birthday. Second molars typically erupt anywhere between 19 months and 3 years of age. Since these molars are large and square compared to your toddler’s anterior teeth (the teeth they use to bite rather than chew), it might seem like they would cause more discomfort—but in fact, you may not even realize when these teeth erupt. Many toddlers present with minimal symptoms with the eruption of these teeth.
First year molars typically come in between 13 to 19 months. Toddlers stop teething by three years old, although they may stop teething even before, depending on when their two-year molars fully emerge. By this time, your toddler will have developed all 20 baby teeth, which are also known as primary teeth. To compare, adults have 32 teeth, including 12 molars (4 of which are wisdom teeth) and 8 premolars.
Toddler Teething Symptoms
- Individual Reactions: Each child experiences teething pain differently; past remedies can be helpful for soothing.
- Communication: Encourage toddlers to express discomfort using signs or basic words.
- Pain Misinterpretation: Teething can mimic ear infections, especially with posterior molar eruption leading to ear pain.
- Consult Pediatrician: Persistent fever, lethargy, or ear drainage may indicate an ear infection.
- Teething Indicators: Tugging on ears, finger sucking, and increased drooling without other symptoms suggest teething.
- Fever:
- A minor fever may occur during teething but should not exceed 101°F.
- If a fever exceeds 101°F or lasts more than a few days, consult a pediatrician.
- Nighttime Symptoms:
- Teething pain may seem worse at night; this may be due to tiredness rather than increased pain.
- Tiredness can lead to crankiness, amplifying teething symptoms.
- Two-Year Molars:
- Ear pain and minor temperature may occur during eruption.
- Symptoms lasting 3-5 days likely indicate something other than teething.
Feeding During the Two-Year Molars
While your teething toddler’s molars are growing, chewing might cause pain. Your child might drool more and become fussy more quickly during mealtime. Plan meals around their symptoms—choose foods that are easy to swallow and don’t take a lot of work to eat. Here are a few food ideas for your teething toddler:
Smoothies. Turn mealtime into a treat that’s soft and cold for your teething toddler’s gums. Smoothies are quick to make if you have frozen food on hand and can be a nutritious breakfast option for your toddler. You can even include dark green veggies like kale and spinach.
Mashed bananas. Even easier to prepare than smoothies, mashed bananas can be mashed with a fork or potato masher. Use fresh or frozen bananas and add a nut butter for a protein boost.
Soups or stews. Healthy, vegetable-filled soups and stews are easy to eat options for your toddler. Opt for smoother soups rather than chunky ones that require more chewing.
Pureed fruits and veggies. Pureed fruits and vegetables don’t need to be chewed, so this may be an ideal choice during periods of discomfort.
Frozen fruit. When flash frozen, produce contains the same nutritional value as its fresh counterpart. Frozen sliced grapes and frozen cherries are great options for finger-friendly snacks, and the cold temperature will be soothing for your teething toddler.
Chilled applesauce. Put this snack standby in the refrigerator before serving to your toddler for a cool, sweet dessert.
FAQs on Toddler Teething
1. What are the common symptoms of toddler teething?
Common symptoms include:
- Increased drooling
- Gum sensitivity or swelling
- Irritability or fussiness
- Chewing on objects or fingers
- Difficulty sleeping
2. What foods are best for teething toddlers?
Soft, easy-to-eat foods like smoothies, mashed bananas, pureed fruits and vegetables, soups, and chilled applesauce are ideal for toddlers experiencing teething discomfort.
3. How can I differentiate between teething and an ear infection?
Teething pain can radiate to the ears, but ear infections often come with additional symptoms such as:
- Persistent fever
- Lethargy
- Ear drainage
If you observe these symptoms, consult a pediatrician.
4. How can I soothe my toddler’s teething discomfort?
You can try:
- Offering cold foods like chilled applesauce or frozen fruits
- Providing a cold teething ring or washcloth
- Gently massaging their gums
- Using over-the-counter pain relief as advised by a pediatrician
When Should I See a Pediatrician or Dentist?
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends a call to the doctor or an emergency room visit if your child has a fever above 104°F, if your child’s fever has lasted longer than five days or if fever-reducing medicines do not reduce the fever. Take behavior and activity level into account, too. Observe how your child behaves and whether they’re acting like themselves.
Knowing the symptoms and the timeline for your toddler’s teething will help you be prepared when the two-year molars erupt. Teething symptoms like gum and ear pain can be remedied by soft, cool foods. Once your toddler has all 20 of their baby teeth, it’s now time to keep the teeth healthy and strong. Before you know it, they’ll be losing their baby teeth and developing their first adult teeth: the six-year molars.
For more information about Dr. Reena’s work at Growing Smiles, please visit the Growing Smiles website.


